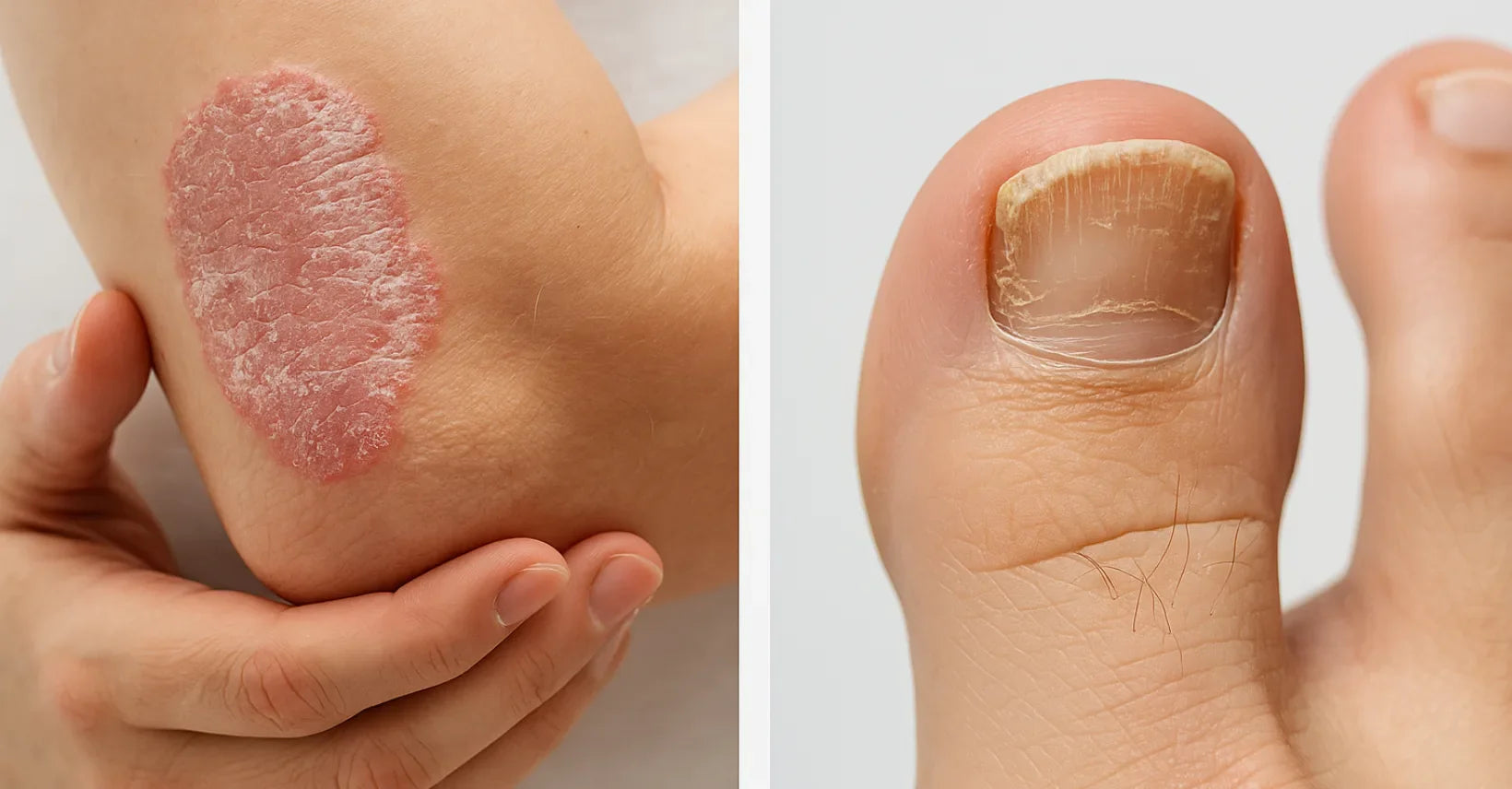
Psoriasis vs. Fungal Infection: How to Tell the Difference
Imagine this: you notice a red, itchy patch on your skin. You immediately start wondering—is it psoriasis, or could it be a fungal infection? Both conditions can cause discomfort, and at first glance, they might look surprisingly similar. But while one is an autoimmune condition that lingers long-term, the other is caused by microscopic fungi that can often be treated and cleared. Knowing the difference isn’t just about comfort—it’s about getting the right treatment and preventing flare-ups or recurrences.
Let’s break down Psoriasis vs. Fungal Infection in detail so you can spot the differences with confidence.
Knowing whether your skin issue is psoriasis or a fungal infection matters, because the treatment paths are different—fungal infections often respond well to solutions. Buy fungus solution and see the results within a week.
Understanding Psoriasis

Before we dive into comparisons, it’s important to understand what psoriasis actually is. Psoriasis is not contagious—it’s a chronic condition that affects the way your skin regenerates. Instead of shedding old cells gradually, the skin renews too quickly, leading to a buildup of thick, scaly patches.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack healthy skin cells. This leads to rapid turnover of skin, which shows up as inflamed, scaly, or silvery patches. These patches may itch, burn, or cause discomfort. Triggers can include stress, infections, cold weather, and even certain medications.
Common Types of Psoriasis (Plaque, Guttate, etc.)
Psoriasis doesn’t look the same for everyone. Some common forms include:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, showing thick, raised patches with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Appears as small, drop-like red spots, often triggered by infections.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Found in skin folds, such as under breasts or around the groin.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by pus-filled bumps surrounded by red skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare, severe form causing widespread redness and shedding of skin.
Understanding Fungal Infections
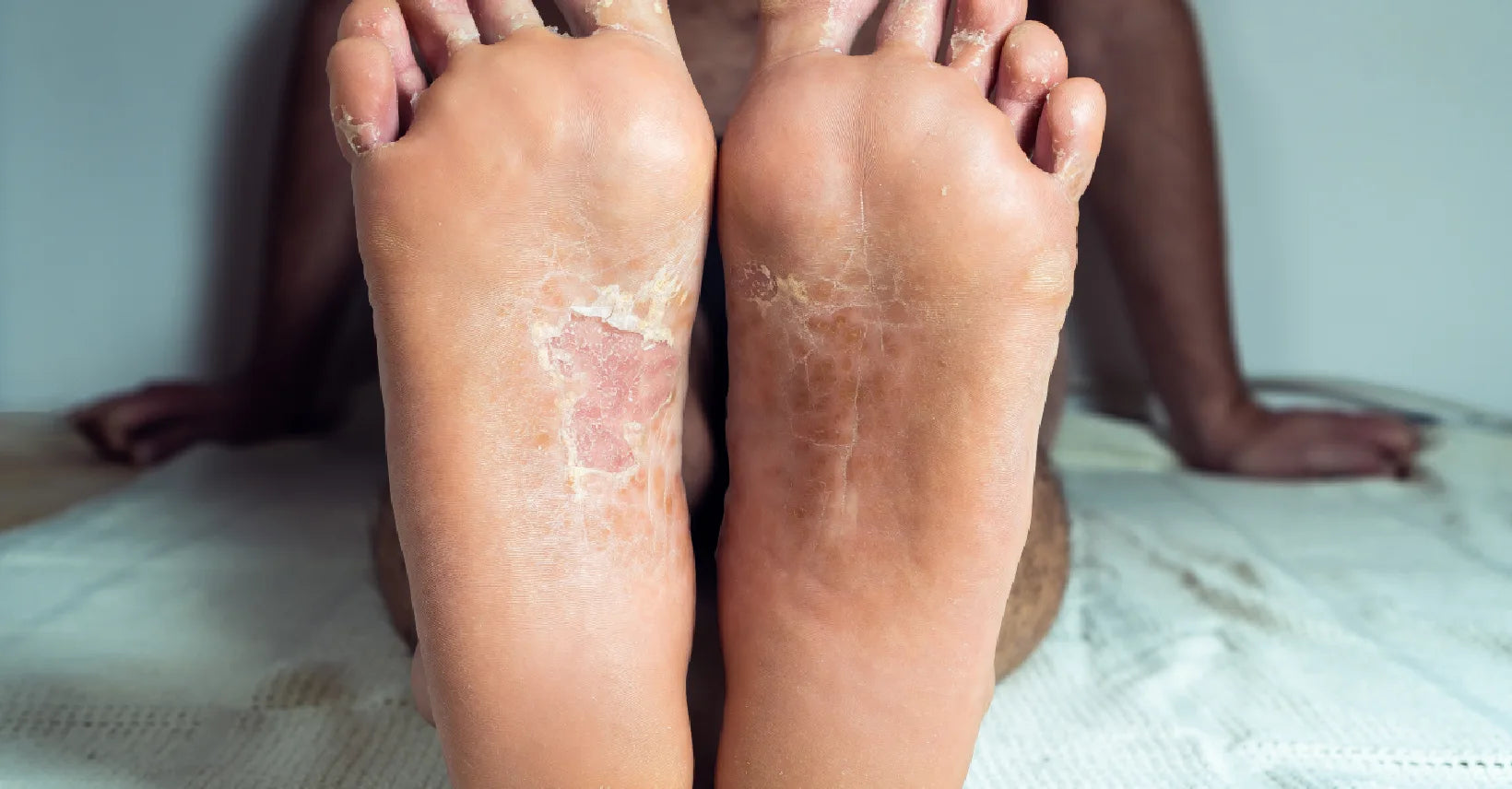
Now, let’s look at the other side of the puzzle: fungal infections. Unlike psoriasis, fungal infections are caused by living organisms—fungi—that thrive in warm, moist environments. They can spread from person to person, or even from pets, surfaces, or contaminated clothing.
What is a Fungal Skin Infection?
A fungal skin infection happens when fungi invade the outer layers of your skin, nails, or scalp. They often cause red, itchy, ring-like rashes that may spread without treatment. Unlike psoriasis, fungal infections are contagious, and hygiene plays a big role in prevention.
Common Types (Ringworm, Athlete’s Foot, Yeast Infection, etc.)
There are many kinds of fungal infections, but the most common ones include:
- Ringworm (Tinea): A circular rash that looks like a ring.
- Athlete’s Foot: Itchy, peeling skin between the toes.
- Jock Itch: A fungal rash in the groin area.
- Yeast Infections (Candida): Often in warm, moist skin folds.
- Nail Fungus: Thick, brittle, and discolored nails.
Since fungal infections often affect the nails too, you might also find our guide on "Does Alcohol Kill Toe Fungus?" useful for deeper insight.
Psoriasis vs. Fungal Infection – Key Differences

At first glance, psoriasis and fungal infections can look alike. But here’s where they differ:
- Cause: Psoriasis is autoimmune; fungal infections are caused by fungi.
- Appearance: Psoriasis often has thick, silvery scales; fungal infections usually have a red, ring-shaped rash.
- Symptoms: Psoriasis may cause pain, burning, or itching. Fungal infections mostly cause itching and spreading redness.
- Contagious: Psoriasis is not contagious, but fungal infections spread easily.
- Treatment: Psoriasis often needs long-term management with creams, phototherapy, or medication. Fungal infections are treated with antifungal creams, powders, or oral medicine.
Understanding these differences is key to preventing misdiagnosis and ensuring the right treatment.
When dealing with fungal infections, lifestyle and nutrition play a role too, which we cover in our blog on the Best Supplements for Fungal Infections.
Final Thoughts on Psoriasis vs. Fungal Infection
When you spot unusual skin changes, it’s easy to assume it’s just a rash. But as we’ve seen, Psoriasis vs. Fungal Infection is more than a cosmetic issue—they are two very different conditions that need different treatments. If you’re ever unsure, it’s best to consult a dermatologist. Proper diagnosis is the first step toward relief and healthy skin.
FAQ
1. Can Psoriasis Be Mistaken for a Fungal Infection?
Yes—psoriasis and fungal infections can look similar, with red, itchy patches commonly being misinterpreted. Psoriasis tends to have thicker, silvery scales, while fungal infections often form ring-shaped rashes that grow if left untreated. Diagnosis may require a skin scraping.
2. Is it possible to have both Psoriasis and a Fungal Infection at the same time?
Yes, it absolutely is. People with psoriasis can also develop fungal infections, sometimes right at the site of psoriasis flare-ups.This overlapping occurrence further complicates diagnosis and treatment, so consulting a dermatologist is key.
3. How can you identify a fungal infection compared to psoriasis?
Fungal infections often present as small, red, itchy patches with a distinct border and central clearing—think ring-like shapes. In contrast, psoriasis typically causes raised, scaly plaques with silvery or thick scales and no clear borders
4. What is the KOH test, and how does it help in distinguishing between Psoriasis and Fungal Infections?
The KOH (Potassium Hydroxide) test is a quick and inexpensive diagnostic tool. A clinician scrapes skin or nail samples, applies KOH solution, and examined under a microscope. Fungal elements such as hyphae or spores will be visible if it's an infection—while they won't appear in psoriasis.
5. Are there specific risk factors for fungal infections versus psoriasis?
Yes. Fungal infections thrive in warm, moist conditions and can spread via contact, especially in communal places like locker rooms or showers. Common risk factors include excessive sweating, compromised skin integrity, shared personal items, and contact with infected surfaces or individuals. Psoriasis, in contrast, is largely driven by autoimmune factors and can be triggered or worsened by stress, cold or dry weather, smoking, and skin injuries
Share

